

Its being seen on CT or/and MRI scans of the brain. those that are regularly interrupted (e.g. prominence of sulci, sulvian fissures cerebellar folia and basilar cisterns MEANS Its a sign of (severe) cerebral atrophy.
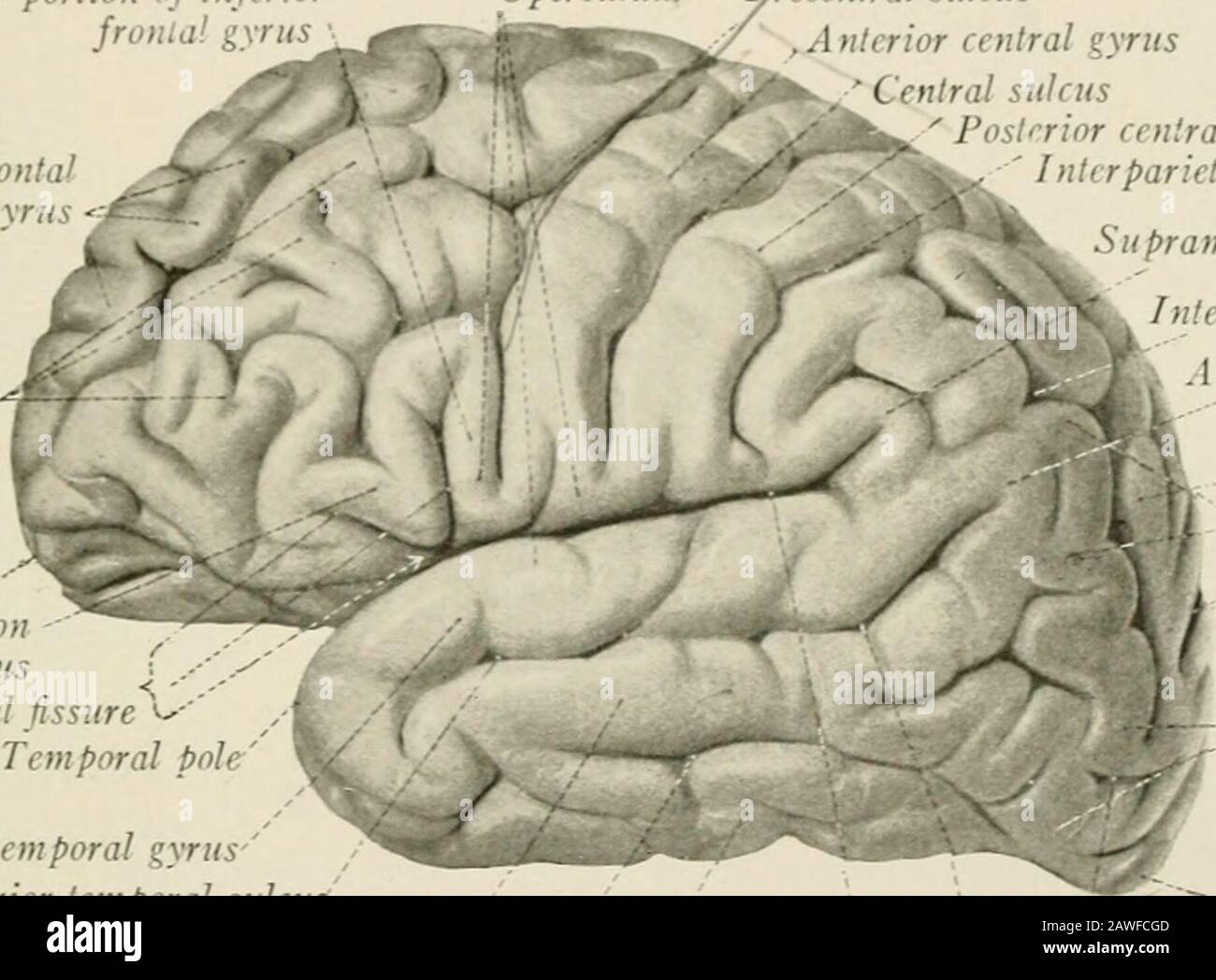
those that have low interruption rates (e.g.The cerebellum is neuron-rich, containing 80 of the brain’s neurons organized in a dense cellular layer. lateral sulcus, which results from the relatively slow growth of the insular cortex and the submersion of the adjoining frontal, parietal and temporal areas) A deep horizontal fissure found within the posterior lobe separates the superior and inferior surfaces of the cerebellum. Marieb & Hoehn (Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9th ed.). commonly continuous or uninterrupted (e.g. Figure 3: Lobes, sulci, and fissures of the cerebral hemispheres (longitudinal fissure not pictured).On the basis of continuity (whether the sulci are broken into segments by gyral bridges crossing them) 2: the splenium of the corpus callosum conveys a large number of fibers from the temporal and occipital cortices to the parietal-occipital sulcus creating a number of axial and limiting sulci within the wall of the parieto-occipital sulcus) secondary sulcus: sulci formed within others due to the continued growth of adjoining areas of the cortex (e.g.primary sulcus: formed before birth (e.g.operculated sulcus: a sulcus may be between two structurally different areas and a third sulcus may lie in its wall and does not appear on the surface (e.g.axial sulcus: some sulci develop along the axis of a rapidly growing/developing area (e.g.limiting sulcus: some sulci develop between areas differing in structure and function (e.g.Sulci can be divided on the basis of function 3: Sulci develop at the end of the 3rd fetal month 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
